Climate Policy Costs, Regional Politics and Backlash against International Cooperation
Abstract
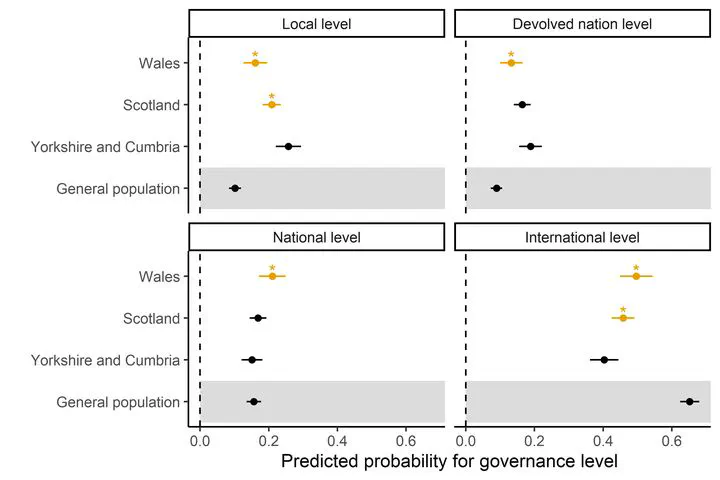
This paper investigates the conditions under which subnational concerns shape public assessments of international climate governance. In line with existing literature, we maintain that costly policy adjustments fuel negative views of international cooperation in policy exposed regions. At the same time, we argue that the more resentful relations are with the national center of politics, the more sympathetic these regions are to international institutions and global governance. Based on geographically targeted survey data from the United Kingdom, we find that fossil fuel-intensive regions with strong, institutionalized regional politics have more positive assessments of international climate cooperation than structurally similar regions where regional political institutions are less pronounced. The findings show that regional politics characteristics are key for understanding climate policy beliefs among citizens that bear the brunt of adjustments to international climate agreements.
Type
Publication
British Journal of Political Science 55: e132